
The only thing I miss is the latter.ĭf <- round ( as. In the end I want a data frame consisting of alphas, r-squared values and t-values for all of my alphas. $ operator is invalid for atomic vectors.
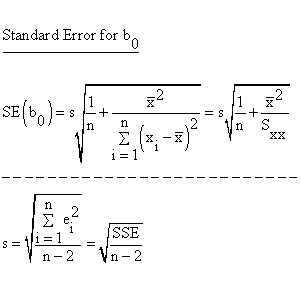
CALCULATE STANDARD ERROR OF SLOPE CODE
When I use the same code trying to extract t-values (lapply(summary(fit),”), but end up with this error code: Error in summary(fit)$coefficients : Lapply(summary(fit),”[[“,”r.squared”), and ended up with a list of 9 r-squared values which I converted to a numeric object before making a data frame of it. When I extracted the r-squared I used the lapply function, like this: When I apply summary(fit) I get 9 regression outputs, including all the summary statistics like residuals, coefficients (estimate, std error, t-value, p-value) as well as r-squared and adj r-squared. When I print the fit object I get the intercept (alpha) and the slope (beta) of each X-value, for each dependent variable, ie 9 columns with alpha, slope X1, slope X2 and slope X3. Don’t hesitate to let me know in the comments section, in case you have further questions.
CALCULATE STANDARD ERROR OF SLOPE HOW TO
In summary: At this point you should know how to return linear regression stats such as standard errors or p-values in R programming.
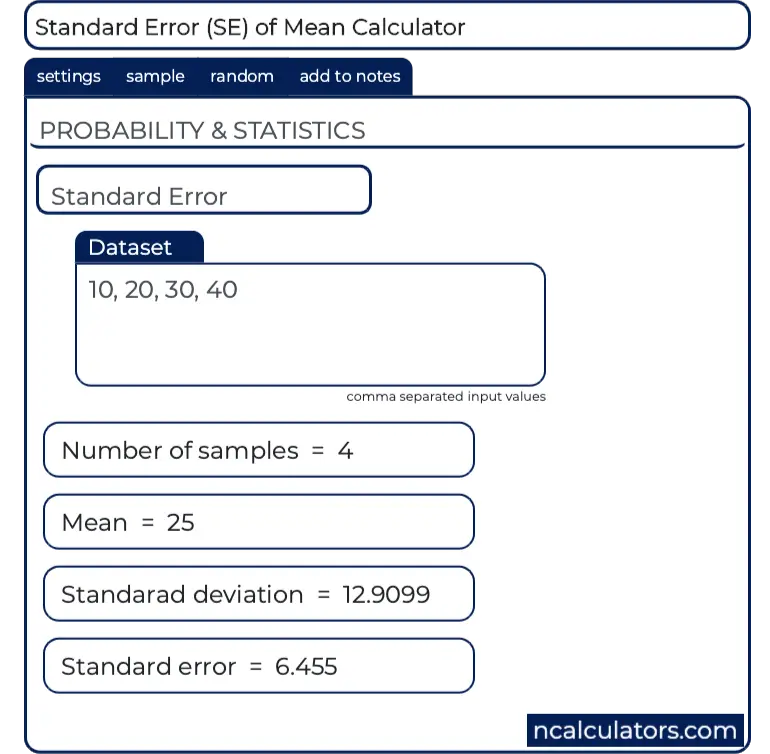

The variable y is our target variable and the variables x1-圆 are the predictors.
# 6 1.74 1.68 1.61 -0.63 -3.16 -0.21 0.31Īs you can see based on the previous RStudio console output, our example data is a data frame containing seven columns. Head(data) # Showing head of example data Set.seed(1234421234) # Drawing randomly distributed data seed ( 1234421234 ) # Drawing randomly distributed data


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
